What Do Animal Cells Contain That Plant Cells Don't Yahoo
Chief Difference – Found vs Animate being Cells
Plant cells and creature cells are two types of eukaryotic cells. Thus, both these cell types are composed of membrane-bound organelles like nucleus, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Both cell types contain 80S ribosomes for protein synthesis. Plant cells exhibit a fixed, rectangular shape due to the presence of a prison cell wall. Their cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose. On the opposite, animal cells accept a round, irregular shape due to the absence of a prison cell wall. The cardinal difference betwixt plant and animal cells is that plant cells are composed of jail cell walls and chloroplasts whereas animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts.
This article studies,
1. What are Plant Cells
– Structure and Characteristics
2. What are Animal Cells
– Structure and Characteristics
3. What is the difference betwixt Plant and Animal Cells
What are Plant Cells
Constitute cells belong to the kingdom: Plantae. One of the characteristic features in institute cells is the cellulose cell wall they carry. Establish cell wall is mainly composed of different compounds such every bit cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin and lignin. These compounds are secreted by protoplast in the cell membrane. The prison cell wall provides the shape to form tissues of the plant and plays a vital role in intercellular communication, in improver to providing protection. The cell wall helps to form plant-microbe interactions. Plasmodesmata is a specialized prison cell-to-prison cell communication pathway that is created through the pores in the chief cell wall. Plasmalemma and endoplasmic reticulum of the adjacent cells are continuous through the plasmodesmata.
On the other mitt, found cells consist of a big, central vacuole. The membrane of the vacuole is called the tonoplast. Water-filled vacuole maintains prison cell's turgor and helps to control the movement of molecules between the cytosol and the sap. Ultimately, the vacuole stores digested waste proteins and organelles and other useful fabric.
Another major characteristic in found cells is their ability to produce carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water with the aid of sunlight. This procedure is called photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is the green-colored pigment which absorbs the dominicus light. It occurs in plastids identified equally chloroplast.
On the other mitt, amylplasts are some other plastid type which is specialized for the storage of starch. Elaioplasts are specialized for the storage of fat. Pigments are synthesized and stored in chromoplasts. Plastids are composed of their own genomes with about 100 to 120 unique genes in it. Plastids are thought to be originated from prokaryotic endosymbionts found in early on ancestor eukaryotes.
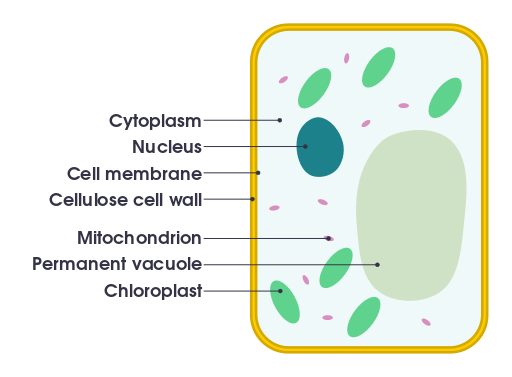
Effigy 1: Generalized Plant Cell
What are Animal Cells
Multicellular cells belonging to the kingdom: animalia are referred to as animal cells. Approximately 210 distinct prison cell types can be constitute in developed human torso. They have diverse functions like production of enzymes, hormones and product of energy. Animal cells are smaller in size compared to found cells. They are irregular in shape due to the lack of a cell wall. The outer boundary of an animate being cell is the plasma membrane which is considered as semi-permeable. Semi-permeable membranes only allow selected molecules to move beyond it. Plasma membrane is composed of phospholipids containing polor heads and non-polor tails. It is described by the lipid bi-layer model. Animal cells too lack a big vacuole also as plastids. They comprise structures like cilia, centrioles, flagella and lysosomes. Lysosomes shop digestive enzymes.
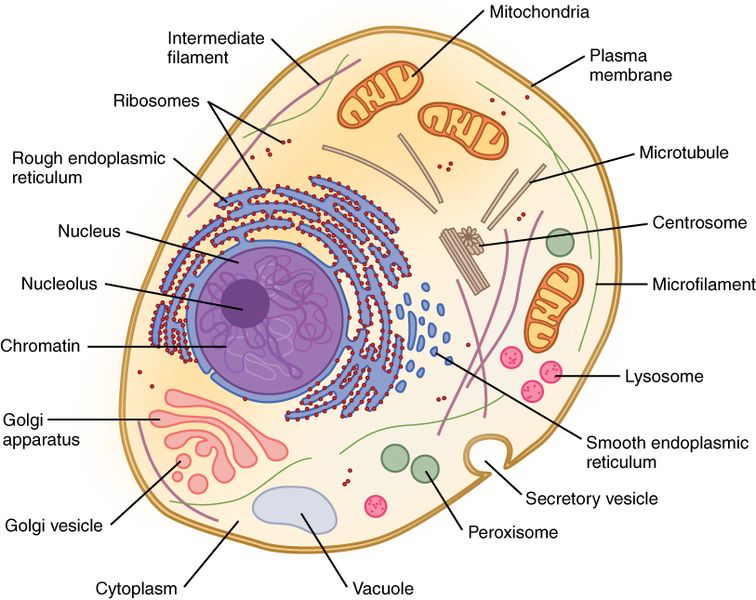
Figure ii: Generalized Animal Cell
Difference Between Found and Animal Cells
Cell Wall
Plant Cells: Institute cells are composed of a prison cell wall made up of cellulose.
Animal Cells: Beast cells don't possess a prison cell wall. Thus, animal cells can change the shape of the cell often.
Size of the Cell
Institute Cells: Plant cells are usually larger in size.
Animal Cells: Animal cells are comparatively smaller in size.
Shape
Found Cells:Fauna cells accept a rectangular, fixed shape.
Animal Cells:Plant cells have a round, irregular shape.
Vacuole
Plant Cells: They have 1 or more, comparatively very smaller vacuoles.
Animal Cells:They have 1, large, key vacuole taking 90% of cell volume.
Centrioles
Institute Cells: Centrioles are present in lower forms of plants.
Animal Cells: Centrioles are present in all animals.
Cholroplast
Plant Cells: Institute cells are composed of chloroplast to produce their own food. Hence, establish cells are autotophs.
Animal Cells: Animals cells do not comprise chloroplast. Hence, animal cells are heterotrophs.
Lysosomes
Plant Cells: They don't have lysosomes.
Creature Cells:They consist of lysosomes in the cytoplasm.
Glyoxysomes
Found Cells: They are composed of glyoxysomes.
Beast Cells: They don't accept glyoxysomes.
Junctions
Found Cells:They are equanimous of plasmodesmata every bit cell junctions.
Animal Cells: Tight junctions and desmosomes are nowadays as junctions.
Food Reservation
Plant Cells: They reserve food in the form of starch.
Animal Cells: They reserve food in the form of glycogen.
Amino Acrid and Coenzyme Synthesis
Plant Cells: Establish cells synthesize all required amino acids, coenzymes and vitamins by themselves.
Animal Cells: Animal cells are unable to synthesize all amino acids, coenzymes and vitamins required by them.
Spindle Germination
Plant Cells: Spindle formation is anastral.
Animal Cells: Spindle formation is amphiastral.
Prison cell Burst
Plant Cells: Plant cells do not burst under hypotonic weather condition due to the presence of cell wall.
Creature Cells: Animal cells volition burst nether hypotonic conditions.
Conclusion
The basic structure of constitute and brute cells are comparatively the same. Animal cells are smaller than plant cells. They also consist of an irregular shape. Therefore animal cells can act as transporters. The well-nigh common example is ruby-red blood cells in human circular system. On the other hand, constitute cells contain plastids called chloroplast for photosynthesis. But, animal cells practise not contain chloroplasts. Thus, plant cells are considered as autotrophs whereas the animal cells are considered as heterotrophs. This is the principal departure between plant and brute cells.
Reference:
1. "Institute prison cell". Wikipedia, the gratuitous encyclopedia, 2017. Accessed 22 February 2017
two. "Plant Prison cell Anatomy". Encharnted Learning, 2016. Accessed 22 Feb 2017
three. "Animal Jail cell Structure". MOLECULAR EXPRESSIONS, 2015. Accessed 22 February 2017
iv. "Animal jail cell". TutorVista.com, 2017. Accessed 22 Feb 2017
Image Courtesy:
ane. "Simple diagram of plant cell (en).svg". Past domdomegg – Own work (CC-By-4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ii. "0312 Animal Prison cell and Components.jpg". By OpenStex – (CC-Past-4.0) via Commons Wikimedia

Source: https://pediaa.com/difference-between-plant-and-animal-cells/
Posted by: rossarman1993.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Do Animal Cells Contain That Plant Cells Don't Yahoo"
Post a Comment